Aphthous Ulcer of Tonsil & American Family Physicians
| Uvula | |
|---|---|
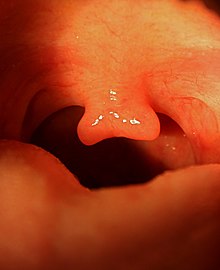
 Rima oris of a kid showing the uvula and swollen tonsils | |
| Details | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Location | Mouth |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | uvula palatina |
| MeSH | D014609 |
| TA98 | A05.2.01.004 |
| TA2 | 2781 |
| FMA | 55022 |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
The palatine uvula, commonly referred to as simply the uvula, is a conic projection from the back border of the middle of the soft palate, composed of connective tissue containing a number of racemose glands, and some muscular fibers.[1] [2] Information technology as well contains many serous glands, which produce sparse saliva.[3]
Structure [edit]
Muscle [edit]
The muscular function of the uvula (Latin: musculus uvulae) shortens and broadens the uvula. This changes the profile of the posterior office of the soft palate. This change in contour allows the soft palate to adjust closely to the posterior pharyngeal wall to help close the nasopharynx during swallowing.[4]
Its muscles are controlled by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve.
Variation [edit]
The bifid uvula of a 24-year-former adult female
A bifid or bifurcated uvula is a split or cleft uvula. Newborns with cleft palate often too have a split uvula. The bifid uvula results from incomplete fusion of the palatine shelves just information technology is considered simply a slight grade of clefting. Bifid uvulas have less muscle in them than a normal uvula, which may cause recurring bug with middle ear infections. While swallowing, the soft palate is pushed backwards, preventing food and drink from inbound the nasal cavity. If the soft palate cannot bear on the back of the throat while swallowing, food and drinkable can enter the nasal cavity.[v] Splitting of the uvula occurs infrequently but is the most common class of mouth and nose area cleavage among newborns. Bifid uvula occurs in about ii% of the full general population,[vi] although some populations may have a loftier incidence, such as Native Americans who have a 10% rate.[vii]
Bifid uvula is a common symptom of the rare genetic syndrome Loeys–Dietz syndrome,[8] which is associated with an increased run a risk of aortic aneurysm.[ix]
Office [edit]
During swallowing, the soft palate and the uvula move together to shut off the nasopharynx, and prevent food from inbound the nasal cavity.
It has also been proposed that the abundant amount of thin saliva produced by the uvula serves to continue the throat well lubricated.[3]
It has a part in voice communication also. In many languages, the uvula is used to articulate a range of consonant sounds, known as uvular consonants. The voiced uvular trill, written [ʀ] in the International Phonetic Alphabet, is one example; it is used in French, Arabic and Hebrew, among other languages. Due to the large amount of saliva produced from glands in the uvula that are absent in other mammals, it has been suggested that the uvula is an accessory speech organ.[ten]
Stimulation of the uvula besides causes the gag reflex to initiate. This is often a trouble for people with uvula piercings, and a common method of inducing vomiting.[ citation needed ]
Clinical significance [edit]
Inflammation [edit]

A swollen uvula with additional upper oral fissure ulcer in a run-down developed (common cold)
At times, the mucous membrane around the uvula may swell, causing the uvula to expand 3–5 times its normal size. This status is known as uvulitis. When the uvula touches the throat or natural language, it can crusade sensations like gagging or choking, although there is no foreign matter present. This tin cause issues with breathing, talking, and eating.
There are many theories well-nigh what causes the uvula to swell, including dehydration (e.thou. from arid weather condition); excessive smoking or other inhaled irritants; snoring; allergic reaction; or a viral or bacterial infection. An aphthous ulcer which has formed on the uvula can also cause swelling and discomfort.[xi]
If the swelling is caused past dehydration, drinking fluids may amend the condition. If the cause is a bacterial infection, gargling salt water may help. However, it can also be a sign of other bug. Some people with a history of recurring uvulitis comport an epinephrine autoinjector to counteract symptoms of an attack. A swollen uvula is not normally life-threatening and subsides in a short time, typically inside a day.
Snoring and sleep apnea [edit]
The uvula can also contribute to snoring or heavy breathing during sleep; having an elongated uvula can cause vibrations that lead to snoring. In some cases this can pb to slumber apnea, which may be treated by removal of the uvula or part of it if necessary, an functioning known as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (unremarkably referred to every bit UPPP, or UP3). However, this operation tin also cause sleep apnea if scar tissue forms and the airspace in the velopharynx is decreased. The success of UPPP as a handling for sleep apnea is unknown, but some enquiry has shown 40–60% effectiveness in reducing symptoms.[12] Typically apnea subsides for the curt term, but returns over the medium to long term, and sometimes is worse than it was before the UPPP.[ citation needed ]
Velopharyngeal insufficiency [edit]
In a small number of people, the uvula does not close properly against the dorsum of the throat, causing a condition known as velopharyngeal insufficiency. This causes "nasal" (or more properly "hyper-nasal") speech communication, where extra air comes down the nose, and the speaker is unable to say certain consonants, such as pronouncing 'b' like 'k'.
Nasal regurgitation [edit]
During swallowing, the soft palate and the uvula move superiorly to close off the nasopharynx, preventing nutrient from entering the nasal cavity. When this process fails, the issue is called nasal regurgitation. Information technology is common in people with VPI, the myositides, and neuromuscular illness. Regurgitation of fluids in this manner may besides occur if a particularly high book of liquid is regurgitated, or during vigorous coughing, for example being caused by the accidental inhalation of h2o. Due to the action of coughing preventing the uvula from blocking the nasopharynx, liquid may exist expelled back through the nose.
Lodge and culture [edit]

A kid'southward bloated uvula with tonsils
In some parts of Africa, including Ethiopia and Eritrea, the uvula or a section of information technology is ritually removed by a traditional healer.[13] In this instance, the uvula may be noticeably shortened. Information technology is not thought to contribute to velopharyngeal inadequacy, except in cases where the tonsils have besides been removed.[14]
History [edit]
Etymology [edit]
In Latin, ūvula ways "little grape", the diminutive form of ūva "grape" (of unknown origin). A swollen uvula was chosen ūva.[15]
See also [edit]
- Uvula (disambiguation)
- Tonsil
- Epiglottis
References [edit]
- ^ "eMedicine Definition". Archived from the original on 2008-02-16. Retrieved 2008-05-03 .
- ^ 10 Cate's Oral Histology, Nanci, Elsevier, 2007, page 321
- ^ a b Dorsum, GW; Nadig, S; Uppal, South; Coatesworth, AP (December 2004). "Why do nosotros have a uvula?: literature review and a new theory". Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences. 29 (vi): 689–93. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2273.2004.00886.x. PMID 15533161.
- ^ Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 108
- ^ "Split up Uvula: Is It a Trouble?". Retrieved 23 September 2007.
- ^ Shu, One thousand.D., Jennifer (April 12, 2010). "Volition a bifid uvula cause whatsoever problems?". CNN. Retrieved 2010-08-07 .
- ^ McMillan, Julia A.; Feigin, Ralph D.; DeAngelis, Catherine; Jones, M. Douglas (2006). Oski's pediatrics: principles & practice (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 469. ISBN978-0-7817-3894-i.
- ^ "Loeys-Dietz Syndrom Foundation". Archived from the original on 5 Baronial 2012. Retrieved 25 March 2010.
- ^ Vilacosta, Isidre; Godoy, Victoria Cañadas (2008). "Bifid Uvula and Aortic Aneurysm". New England Periodical of Medicine. 359 (2): e2. doi:x.1056/NEJMicm070582. PMID 18614778.
- ^ Finkelstein Y, Meshorer A, Talmi Y, Zohar Y, Brenner J, Gal R (1992). "The riddle of the uvula". Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 107 (3): 444–50. doi:x.1177/019459989210700318. PMID 1408233. S2CID 25135787.
- ^ Biblo LA, Gilbert IA (May 1983). "Aphthous ulcer of the uvula and the painful burp". North. Engl. J. Med. 308 (nineteen): 1168. doi:10.1056/NEJM198305123081922. PMID 6835348.
- ^ Lehnert, Paul (3 August 2005). "Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty for obstructive sleep apnea". Retrieved 26 Oct 2006.
- ^ Ethiopian Refugees
- ^ Hartley B, Rowe-Jones J (1994). "Uvulectomy to prevent throat infections". J Laryngol Otol. 108 (one): 65–half dozen. doi:10.1017/s0022215100125873. PMID 8133174.
- ^ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English language Linguistic communication (4th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin. 2000. p. 1896. ISBN978-0618082308.
External links [edit]
- MedlinePlus Encyclopedia: 001257 - Uvulitis
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palatine_uvula
0 Response to "Aphthous Ulcer of Tonsil & American Family Physicians"
Enregistrer un commentaire